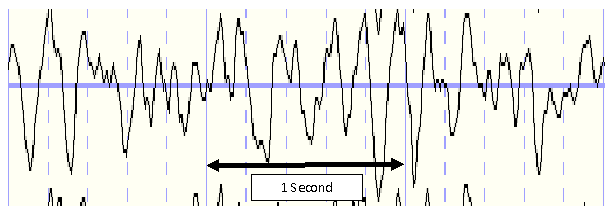
Normal Occurrence of Theta Waves
- Theta waves oscillate about 3.5 – 7.5 times per second (Hz).
- Some consider Theta to be from 4 – 8 Hz.
- Theta is normal in small very amounts in the healthy waking adult EEG.
- Theta in the adult waking EEG should be symmetrically distributed.
- Theta is more prominent and considered normal in the raw EEG’s of children & adolescents unless there is clear indication of pathology.
- Theta at the scalp surface in the adult EEG is normal as part of the early stages of drowsiness.
- Theta may occur in some individuals who are day dreaming.
- Some individuals produce a frontal-midline Theta (FZ) under task conditions that can be recorded at the scalp and is dependent on task difficulty and reflects transfer of information to long-term memory / memory functions
Abnormal Occurrence of Theta Waves
- Excessive Theta activity in the waking raw EEG of adults is considered abnormal. It can represent reduced metabolism cortical grey matter (too little oxygen uptake).
- Theta that is asymmetrically distributed in the waking adult EEG is considered abnormal (more on one side than the other)
- Spike and slow wave complexes that occur in seizure disorder often occur in the Theta frequency range.
- Excessive Theta on quantitative analysis is often seen in conditions such as…
- ADHD
- Learning disabilities
- Head injuries or brain lesions
- Certain neurological disorders
Physiological Origin of Theta Wave Rhythms
- Cortical Theta generation in humans is projected to the cortex via Thalamo-cortical projections and is influenced by GABAergic / Cholinergic inhibitory & excitatory inputs from the Reticular Activating System.
- Cortical Theta is essentially a slowing of the Alpha rhythm but may also be influenced by limbically generated (septo-hippocampul) Theta as described below.
- Sub-cortical Theta Rhythms are prominent in the Hippocampus & Limbic system and result from alternating inhibition / disinhibition between the septal nuclei & hippocampal nuclei.
- Limbic Theta oscillations are caused by alternating inhibition / disinhibition of GABAergic & Cholinergic neurons.
- The hippocampus is part of the “Papez Circle” including the Hippocampus (HIP), Entorhinal Cortex in Temporal Lobes, Sensory areas of the Temporals & Parietals, the Mammillary Bodies of the Hypothalamus, and the Thalamus that are involved in memory consolidation.
Role of Theta Waves in Having a Healthy Brain
- Hippocampal & Limbic Theta are highly involved in the encoding of meaningful events into long-term memory.
- Cortical Theta likely represents a “binding rhythm” that ties functionally related neural networks together in time for coordinated processing of memory storage functions.
- Inducing a Theta state via hypnosis or neurofeedback may aid in anxiety reduction and the processing of traumatic memories such as may occur in PTSD
Images of Theta Waves
Single channel;
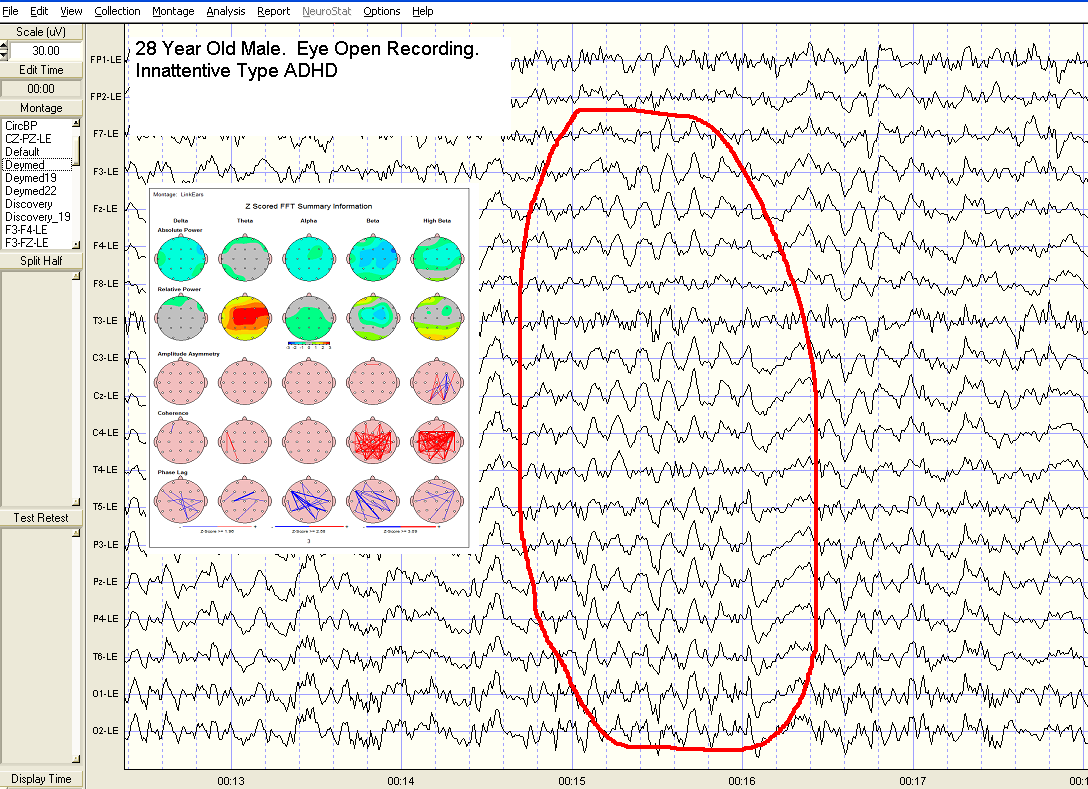
19 Channel: Linked Ear Montage;
28 year old male with ADHD, Inattentive Type. Examples Highlighted in Red
Click here to learn about Alpha Waves >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
EEG Brainwaves
Delta Waves
- Theta Waves
- Normal Occurrence of Theta Waves
- Abnormal Occurrence of Theta Waves
- Physiological Origin of Theta Wave Rhythms
- Role of Theta Waves in Having a Healthy Brain
- Images of Theta Waves