Delta Waves
Normal Occurrence of Delta Waves
- Delta waves are slow EEG waves that oscillate from about .5 to 4 times per second.
- Newer classifications may call Delta .5-2 Hz activity and some may classify Delta as 1 – 4 Hz
- Delta waves tend to be large in amplitude.
- Delta waves are rarely seen in the healthy waking adult EEG but are prominent and normal during sleep, especially of infants, children, and young adults.
- Delta waves are common in infants most of the time (Imagine a baby and how they often nap and doze)
- Delta waves are common in stage 3 & 4 sleep in adolescents and teenagers
- Delta waves begin to disappear from the sleep records of adults after age 45 and tend to be almost entirely absent from those older than age 75.
Abnormal Occurrence of Delta Waves
- Delta should generally be absent from the waking EEG records of adults.
- If Delta appears in the waking EEG record, it may indicate the presence of…
- Head trauma such as might occur in a car accident or bad fall.
- Exposure to toxins such as heavy metals, pesticides, etc.
- Cognitive impairment that might be the result of liver disease or degenerative brain diseases like dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
- Focal Delta may be the result of a lesion or tumor or may indicate damage from a stroke.
Physiological Origin of Delta Wave Rhythms
- Most Delta that is recorded from the scalp in routine EEG is cortically generated and seems to be an intrinsic property of the pyramidal neurons that are primarily responsible for generating the scalp recorded EEG (the cortex is the surface of the Brain).
- Cortical Delta can also be generated by the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus which plays a role in regulating Circadian Rhythms (Sleep / Wake Cycles).
- The Thalamic nuclei also have a role in generating Delta rhythms especially during sleep (the Thalamus is one of the primary pace makers of the brain resulting in the oscillating rhythms seen in the EEG).
- Delta activity during wakefulness in adults is inhibited by the ascending cholinergic neurons from the reticular activating system.
Role of Delta Waves in Having a Healthy Brain
- Delta during sleep is involved in triggering the release of hormones that help the body heal and recuperate.
- Delta during sleep plays a role in transferring new learning and memories into long-term memory storage.
- Interruption of Delta activity during sleep is linked to a variety of disorders including…
- ADHD
- Schizophrenia
- Anxiety & OCD,
- Night Terrors & Sleep walking
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Parkinson’s disease
- Autoimmune disorders such as Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Images of Delta Waves
Single channel;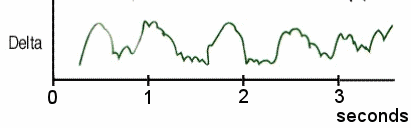 19 Channel: Laplacian Montage;
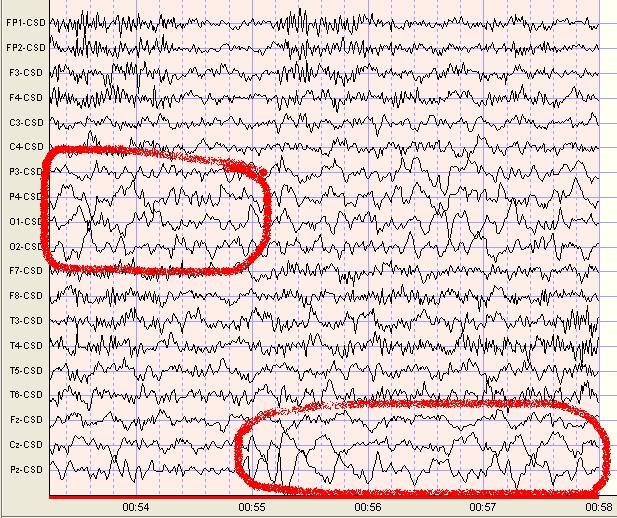
4.9 year old boy with Autism. Note Delta Prominent in Central and Posterior Leads. Examples Highlighted in Red
19 Channel: Laplacian Montage;
4.9 year old boy with Autism. Note Delta Prominent in Central and Posterior Leads. Examples Highlighted in Red
Click here to learn about Theta Waves >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
EEG Brainwaves
Delta Waves
- Delta Waves
- Normal Occurrence of Delta Waves
- Abnormal Occurrence of Delta Waves
- Physiological Origin of Delta Wave Rhythms
- Role of Delta Waves in Having a Healthy Brain
- Images of Delta Waves